Product Requirement for Goods Import and Export
Export and import are the processes of moving goods and services from one country to another. Therefore, there are many requirements before products are allowed to be moved into a country. These requirements depend on the products themselves and the country of origin to ensure that the products meet the standard in a country and do not harm the economic interests, safety, and environmental standards in the destination country.
Some countries have implemented strict standards for imported products to enter their market. These standards have to be done in order to protect the consumers and also the environment in their countries, and most of these countries are developed countries. The requirements for goods include compliance with the local regulations, having complete documentation, having the testing certification, etc. Here are the measures and regulations related to the requirements of exporting and importing goods into a country.
Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures
Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) are the standards of biosecurity as part of product requirements that are implemented by a country to protect the health of humans or animals (sanitary) and plant health (phytosanitary) from imported food products from other countries. This measure is important to verify that the food products are safe to be consumed by citizens and do not harm the livestock and agricultural industries in a specific country.
These standards are mentioned in the World Trade Organization (WTO) about international trade agreements. Therefore, each of the members of the WTO can set up the sanitary and phytosanitary measures. However, the SPS measurement should be accompanied by credible reasons, and it can be proved based on scientific research, not by unfair justification from one country to another, which can lead to a dispute.
SPS for Agricultural goods
SPS for agricultural products is the specific measurement, including the procedure and requirements that are set and implemented by a country for agricultural products. This measurement is to prevent the spread of pests and plant diseases, which can harm certain agricultural commodities in a country. For example, in Australia, everyone who wants to import plants from other countries has to get the Phytosanitary Certificate, which is issued by the National Plant Protection Organisation (NPPO) as a compulsory procedure.
SPS for Processed Foods
SPS for processed foods is the measurement to ensure that the processed food from animals or plant products from other countries meets the health standards in a country. This regulation is compulsory to thwart the public health crisis caused by imported processed food that does not meet sufficient healthy standards. For example, the United States has imposed strict standards and inspections for the prepackaging, the ingredients, food additives, packing materials, etc, of imported processed food from other countries.
SPS for Live animals and Plants
SPS for live animals and plants is a measurement to confirm that the live animals and plants that are intended to enter the country meet the standard. This regulation is established to ensure that all of the live animals and plants brought into a country do not have animal and plant diseases or parasites. For example, the United States requires all live animals to undergo veterinary examination, disease testing, and quarantine before or after being imported.
SPS for Animal feed and Seeds
SPS for animal feed and seeds is the regulation that is set up by a government in a country to verify that all animal feed and seed from other countries are not harmful to the livestock and the farming industries. The animal feed is included in the sanitary regulation because it can spread the disease to animals and risk the animal as well as humans. For example, in Australia, someone who wants to import animal feed from other countries should get permission from the Department of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Forestry.
Technical Regulations
Technical regulations are the legal requisites from the government to confirm that the imported products meet the standard in that country. This mandatory standard is based on the national interest of a country to protect the consumer, ensuring public health, safety standards, etc. These regulations are compulsory; thus, if the goods do not meet one of the requirements, the products cannot enter or are prohibited from being marketed in that country.
For example, the electrical appliances must have a permit from a government agency in a country in order to be imported. These requirements are essential for the safety code standards in the country. If the electrical appliances do not meet the standards in the country, it could be dangerous for the consumer who buys them. In the European Union (EU), electrical appliances must have the CE mark to be sold in the European Economic Area (EEA). This mark indicates that certain products meet the high safety and environmental standards in Europe.
ISO Standards
ISO Standards are the certification standards that are acknowledged worldwide after being assessed by experts from all over the world. These standards are established by the International Organization for Standardization to verify the quality, efficiency, and safety in order to meet the requirements of global trade. These standards can be included in many things, from the process of making products to offering services to satisfy the consumers. Here are the lists of examples of ISO standards that are widely recognized:
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems): This standard system provides a certification for organizations to ensure the consistency and quality of their products and services in order to meet the international standard and be recognized worldwide. This standardization is crucial before managing the documentation and reliability needed in international trade. For instance, the pharmaceutical company must implement the specific acceptable standard that is recognized all over the world. If the company meets this standard, its products can be sold in all of the country without the need to get additional approval to enter the country.
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems): This system is the standardization of environmental responsibilities for a company to be acknowledged globally. ISO 14001 will help the company to meet the standard of green products that comply with global regulations on reducing carbon footprint and promoting sustainability. For instance, the forestry-based company must have the ISO 14001 to ensure that the wood for its products comes from legally logged wood.
- ISO 45001 (Occupational Health & Safety Systems): This standardization has the function to ensure that workers meet the health and safety standards. This system brings trust from the regulatory bodies and the consumers that a certain company can guarantee the safety of its workers. For example, in logistics centers, workers are kept safe by reducing workplace risks and implementing some of the hazardous alleviation measures.
- ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management Systems): This standardization is specifically for companies to meet the safety standards of their food products. This system is needed to implement before exporting food and beverage products to other countries. For example, the food production companies must ensure they meet strict food safety standards to allow them to sell the products worldwide.
- ISO 37001 (Anti-Bribery Management Systems): This standardization is proof that their companies have successfully avoided, detected, and tackled bribery conduct. This certification will boost the company’s credibility in order to maintain international dealings with suppliers, customs, and other parties. For instance, the company that allocated the resources to detect and avoid bribery and corruption to meet ISO 37001 will gain more approval while dealing with other parties. It can also mitigate the destruction caused by bribery or corruption activities.
Labelling Requirements
Labelling requirements are one of the requirements in order to import and export products to a country. The labelling on the package allows the process of exporting and importing certain products to be easy and quick. The customs and the shipping party will easily recognize the origin and the goods that are intended to enter a country. Here are the lists of the labelling requirements in the international trade practice:
- Country of Origin: This requirement is mandatory for most goods in international trade. The country of origin provides clarity and transparency about where the goods come from before entering a country. This labelling also has the function of tracking the shipment process of products.
- Product Identity: This labelling requirement is compulsory to ensure that the package states the name and specifications of the product. Product identity will help customs easily recognize the products before entering the country. It is also impacting the management of the shipping process based on the physical characteristics of the products.
- Contact Information: This requirement is important to make the exporting and importing process easier. Adding the name and address of the importer or a registered distributor is not only mandatory, but also used to ensure that this product is legit and prevent loss. If there are some problems related to the export or import, the customs or distributor will contact the information.
- Ingredients and Composition: This labelling of ingredients should be included on the package as a mandatory requirement to add specific information about the goods. The composition label will help the officers to check certain processed foods and the products that are common allergens, such as gluten, peanuts, and tree nuts.
- Production and Storage: The detailed information of a product’s method and how the products are stored must be included as a labelling requirement. The production labelling should be easily found to know whether it meets the standard or not. These labelling requirements include the production date, shelf life, and storage requirements to reduce the potential damage.
- Mandatory Systems: This is the labelling based on the standards of the country destinations. This label is compulsory to know whether the products are destined for specific countries. For example, the products that are intended to enter the European Union must have the CE mark. On the other hand, Singapore’s Nutri-Grade system dictates labeling content based on product safety and health information.
Packaging Requirements
Packaging requirements are the standard of packaging of products that are destined for a specific country. The packaging process is important in the transportation of products across borders, especially for long-distance shipments. The proper packaging will reduce the potential damage of the products and ensure the hygienic standard requirements in the country. Some countries require a strict packaging standard, such as using non-toxic packaging and having proper labelling. Here are the lists of the packaging requirements:
- Secure Packaging: This is one of the requirements to secure the product from potential damage or rot. The use of appropriate materials in packaging and methods will help to protect goods from outside contamination or during the shipping process. For example, the secure packaging will have a heavy impact on environmental factors on goods, especially during transit and long-distance shipping.
- Material Appropriateness: This requirement needs to be implemented to select the appropriate material for packaging based on the products. Therefore, the chosen packaging materials should be suitable and adjusted for the goods being shipped. For instance, airtight containers for food products are used to prevent contamination and maintain freshness.
- Compliance with Country-Specific Rules: This requirement must be implemented based on the country of origin and destination of the products. The exporter should do some research and adhere to the regulations of the importing country in order to alleviate the rejection. On the other hand, this compliance should be based on the products themselves. For instance, in Australia, the meat exporter should use the packaging material that prevents contamination as stated in the Australian Meat Standard (AS:4696).
- Food Safety Standards: This requirement about food standards differs from one country to another. Some countries require strict safety standards measures for food to enter their countries. Meanwhile, some countries do not strictly implement the high standards to move into their countries. For example, the European Union imposed strict regulations on the packaging of food products to be imported into its countries in order to ensure that the packaging prevents contaminants and does not endanger human health.
- Phytosanitary Regulations: Some countries require specific packaging in order to meet the phytosanitary regulations in their countries. This is used to avoid the spread of infectious diseases that could have a destructive impact on agricultural industries. For example, the United States has rules to use wood packaging material (WPM) to prevent the spread of pests. The package must have been fumigated and heated to control the pests.
- Waste Management: This requirement is introduced by some countries to alleviate the waste from packaging. This also bans the hazardous materials that could be harmful to the environment in certain countries. For example, some countries have mandatory packaging reporting or Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes to encourage waste reduction.
- Documentation: This requirement must be included in the packaging in order to allow the products to set foot in the country. The documentation on packaging ensures all required documents, such as customs permits, invoices, and packing lists, are prepared correctly for import clearance.
Conformity Assessment
Conformity assessment is the process of confirming that the products or services meet the specific requirements and standards. Therefore, this process was implemented by conducting examinations, tests, and audits for the products and services. Conformity assessment is essential for international trade because these procedures ensure that the products or services meet the quality and safety standards to enter the international market. Here are the lists of procedures of conformity assessments:
Verification by Product Specialists: This process has a key function to verify that the products or services are adequate to the standards. This verification process is examined by the independent organizations based on their expertise. This also employs specialists to review various verification activities.
Testing: This process aims to corroborate that the products and services are subjected to examination. This process can be conducted by laboratory testing to assess compliance and other types of examination based on the products themselves.
Inspection: This process of evaluation and viewing the products or services to determine whether they meet the specific standard. Inspection can be a physical inspection of products and an inspection of the condition of manufacturing facilities.
Factory Audits: The audit is a procedure of evaluation to determine whether the factory or the method of production meets adequate standards. This process includes manufacturers’ quality systems and processes, which are audited to ensure they consistently produce compliant quality of goods.
Issuance of a Certificate of Conformity (CoC): This is the certification to prove that the products or services meet the requirements internationally. The CoC is issued upon successful verification and confirmation that the product meets the required standards.
Our Regulation Monitor to find product requirements
Finding the right product requirement based on the products and the destination country is quite challenging. We should look at the latest government information to determine the procedure before importing products. Sometimes this process will make us confused, and we will only find the wrong information related to the regulations of the country.
Now, HS Code Match is offering Regulation Monitor to find the product requirements based on your destination country. This will help you to find the right information about the requirements in order to export some products without needing to look at the government website one by one. In Addition, Regulation Monitor provides accurate data from the government agencies all over the world.
Using the Regulation Monitor is quite easy. You can choose a certain product and the country in the bracket, and then choose the product requirement in the category. Then, click the filter button to show the latest regulation that you are looking for. For example, an apple imported to the United States will look like this.
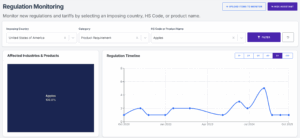
You can click on one of the regulations to see the detailed information. On the regulation detail, you can see the date of the regulation imposed, the regulation summary, the source document, and the text of the information. Additionally, Regulation Monitor also provides the AI Assistant feature if you want to dive deeper into the information instantly.