What are Free Trade Agreements?
A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is a trade agreement between two or more countries to minimize restrictions on exporting and importing products and services. FTA is important to promote trade relations between two or more countries and encourage economic development among the countries. The free trade agreement should be based on mutual recognition and be beneficial for the countries.
Free Trade Agreements can be agreed by the countries in the same region or the countries outside a certain region all over the world. Therefore, FTA is not based only on the regional context, but it can also cover interregional relations based on the bilateral or multilateral relations of countries. However, the neighbouring countries in a region are more likely to conduct intensive business due to the proximity and otherwise.
The implementation of FTA does not mean that the countries should lift all of the barriers and tariffs in trade relations. This agreement only reduces the barriers, and the countries can impose specific rules and restrictions on certain products that they want to enter or export. For example, the United States has reduced the tariff for most of the imported products from Mexico, but it still imposes the tariff for some products, such as aluminum and steel from Mexico
Bilateral Free Trade Agreements
Bilateral Free Trade Agreements (BFTA) are a part of the Free Trade Agreement that is agreed upon by two different countries. As FTA, this trade has a function to eliminate barriers in the trade relations between the members. This agreement aims to boost the economic development between countries by expanding the potential market of the two countries.
Through BFTA, one of the two nations can increase its primary commodities for export to another member country. Otherwise, one of the two nations can receive some commodities that they do not have in order to meet the needs of their country. This agreement is based on comparative advantage and different economic structures, and the mutual benefit of the two countries. Most of the countries that agreed to establish the BFTA are the countries that have a close political and economic relationship and are considered allies.
BFTA is known to be quick to agree because it is only between the two countries. It is also more flexible compared to the multilateral agreement because the negotiation involved only two countries. However, the BFTA tends to be limited and does not have a greater impact on international trade than the multilateral trade agreement. There are examples of BFTA around the world as follows:
United States-Korea Free Trade Agreement (KORUS)
The United States-Korea Free Trade Agreement, or KORUS FTA, is a free trade agreement between the United States and South Korea. This agreement was signed in June 2007, but it was implemented in March 2012 to promote and expand trade between the two nations. Not only does this agreement aim to expand the business between the United States and South Korea, but it also encourages investment.
KORUS FTA has expanded the opportunity for export and import between the United States and South Korea since the two countries are important trade partners. Because of the lower tariffs, small and medium-sized businesses from the United States and South Korea can export their primary commodities. Therefore, this agreement has widened the market for the products and services from the two countries.
Australia-New Zealand Closer Economic Relations Trade Agreements (ANZCERTA)
Australia-New Zealand Closer Economic Relations Trade Agreements (ANZCERTA) is the agreement between Australia and New Zealand. This agreement was signed on 28 March 1983 in order to strengthen the economic relations between these two neighbouring nations in Oceania. ANZCERTA is known as one of the most comprehensive and effective bilateral free trade agreements in the world.
ANZCERTA is established due to the close relationship between Australia and New Zealand. These countries also have similar political and economic interests and are located in the same region. Therefore, Australia and New Zealand need to collaborate to strengthen economic growth and job creation through efficient trade relations.
United Kingdom (UK) and New Zealand (NZ) Free Trade Agreement
The United Kingdom-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement is one of the new trade agreements. This FTA was signed on 28 February 2022 and implemented on 31 May 2023 to encourage the business and economic relations between the UK and New Zealand. This FTA is the most important and comprehensive trade agreement involving New Zealand.
This FTA reflects the close relationship between New Zealand and the UK. This agreement allows New Zealand to easily export its products to be marketed in the UK since the UK is the seventh largest trade partner of New Zealand. Not only benefiting New Zealand, this agreement allows the UK to access the market for some products in New Zealand without a tariff.
Multilateral (or Regional) Free Trade Agreements
The Multilateral Free Trade Agreement (MFTA) is part of the Free Trade Agreement that was signed by three or more nations. Similar to BFTA, MFTA is designed to minimize tariffs and quotas on the exporting and importing process among the member countries. This agreement has a function to enhance the economic and business cooperation among member countries.
MFTA is designed to promote the significant impact of economic development among its member countries. The agreement from many countries, especially in the region, will increase the efficiency of the exporting and importing process among the member countries. This FTA can also eliminate trade diversion and promote development, stability, and prosperity across the region. The multilateral free trade agreement is mostly in a regional context due to the same interests and proximity of a region, or it can be called a regional free trade agreement. However, this type of agreement cannot be limited to the geographical context, but it is based on the political ideology and economic interests of countries. Some countries are involved in a certain FTA even if it is located in a different region.
However, the negotiation of MFTA is considered to be slow and complex due to the need for acceptance by all of the countries. Some of the member countries agree with the new regulations, but if there are one or two countries that do not accept the decision, then the negotiation can be on hold. This situation happens due to the different interests of one country compared to those of others. These are examples of Multilateral Free Trade Agreements around the world, as follows:
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a free trade agreement that was agreed upon by the nations across Southeast Asia. This agreement was developed by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to stimulate economic development and enhance trade across the region. RCEP has also aimed to enhance the participation and friendship of 10 countries in Southeast Asia and 6 other nations in East Asia, South Asia, and Oceania, such as China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, and India.
RCEP is designed to promote the growth of business and investment across nations in ASEAN. Not only enlarge trade and economy among the countries, but it also has the function to settle the disputes on trade across the region. Therefore, this multinational free trade agreement is important due to encouraging fair economic policies that mutually benefit all of the member nations.
Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) is a free trade agreement across the countries in the Pacific region. This FTA includes the countries from Oceania (Australia and New Zealand), the Americas (Canada, Chile, Peru, and Mexico), Southeast Asia (Singapore and Vietnam), East Asia (Japan), and Europe (the United Kingdom). CPTPP was signed by 10 member countries in 2016 and officially implemented in March 2018.
CPTPP has the purpose of reducing tariffs and stimulating business across the Pacific region. This will help all of the members expand their exports and investment to other CPTPP members. Not only for goods, this agreement consists of promoting the digital trade, trade in services, e-commerce, and preventing the violation of intellectual property in all member countries.
African Continental Free Trade Agreement (AfCFTA)
The African Continental Free Trade Agreement (AfCFTA) is a free trade agreement that was introduced by member countries of the African Union (AU). Similar to other free trade agreements, AfCFTA is established to promote trade across African nations to boost economic development. This agreement aims to stimulate the value-added production and enable products from all sectors to be sold easily in other African countries.
AfCFTA was introduced on 21 March 2018 in Kigali, Rwanda, and adopted effectively on 30 May 2019. The most interesting aspect of AfCFTA is that it has 55 member countries, which is deemed the largest free trade agreement in the world. Not only for eliminating the trade barriers, but this agreement also aims to allow investment in order to boost job creation in all of the member nations.
European Union (EU) Single Market agreements
The European Union (EU) Single Market Agreement is a regional free trade agreement among the 27 European Union (EU) member countries and four members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), including Iceland, Norway, Liechtenstein, and Switzerland. This agreement promotes the openness and free movement of goods, services, humans, and capital across Europe. Thus, the EU Single Market will allow people from one of the member countries to set up a small or medium-sized business in other member countries easily.
The EU Single Market benefits all of the companies across Europe that want to invest and market their products, or obtain supplies for their business in the EU and EFTA countries. Meanwhile, the citizens of EU Single Market countries can work, study, and purchase products across the member countries. This agreement will help enhance the job creation and expand business easily across borders in Europe.
United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA)
The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) is an updated free trade agreement from the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). This agreement came into effect on 1 July 2020 to supplant NAFTA, which had been implemented since 1 January 1994. This agreement is put in place to enhance the business and industries across three North American countries, including the United States, Mexico, and Canada. USMCA aims to develop the economy across the border and benefit all of the member countries by promoting fair trade and a free market.
What is an antidumping duty?
Antidumping duty is a duty imposed on products from another country that are sold to the destination country at a lower price than in the home country. This duty is a trade defense instrument that aims to protect the locally produced product in the country. This instrument is usually enforced if the investigations found out that the imported products have a lower price, which will be harmful to the competitiveness in the market.
The investigation of antidumping is conducted by the customs or other government agencies in each country. This process is commonly based on self-initiative from the customs agency, or if a party makes a complaint related to dumping products. Before conducting an investigation, the agency collects sufficient evidence that imported products violate the antidumping policy. Then, the agency collaborated with industry stakeholders to develop the case and launched the investigation. For example, the Canada Border Service Agency (CBSA) and the European Commission are investigating the practice of antidumping from the imported products moved into their territory based on their own initiative and complaints.
What is a countervailing duty?
A countervailing duty is an import tax that is imposed on a product that has a lower price due to subsidies from the government of the origin country. This duty is one of the trade defense instruments that aims to protect domestic producers from unfair imported products. Similar to antidumping, the government agency in every country investigates to tackle the counterveiling action before imposing this duty. For example, the European Commission is responsible for investigating the anti-subsidy practice, and the investigation process commonly takes place within 45 days.
Antidumping and countervailing duties are quite similar, which can harm the local industry and market in a country. However, countervailing and antidumping can be differentiated by the practice itself. Countervailing measures are based on the subsidies that make the cost of production lower and impact the final price of a product. Meanwhile, the antidumping is the practice of selling the product at a lower price in another country than the price in the home country.
Using our HSCodeMatch Application to track Antidumping Measures
For individuals or companies that are involved in international trade, they should be aware of the regulations on international trade imposed by the government of the destination country. This is important in order to ensure that the products destined for the country are not subjected to the antidumping duty. This information is quite hard to find due to being published on the specific government websites, which we sometimes do not know where to find. Therefore, tracking antidumping measures from a country is quite challenging and needs some time.
In order to answer this problem, Jureem HS Code Match provides the feature to track antidumping measures from certain countries. This will help you gather information on the antidumping regulation easily and quickly, without the need to find it one by one from the latest documents published by the official government bodies in a specific country.
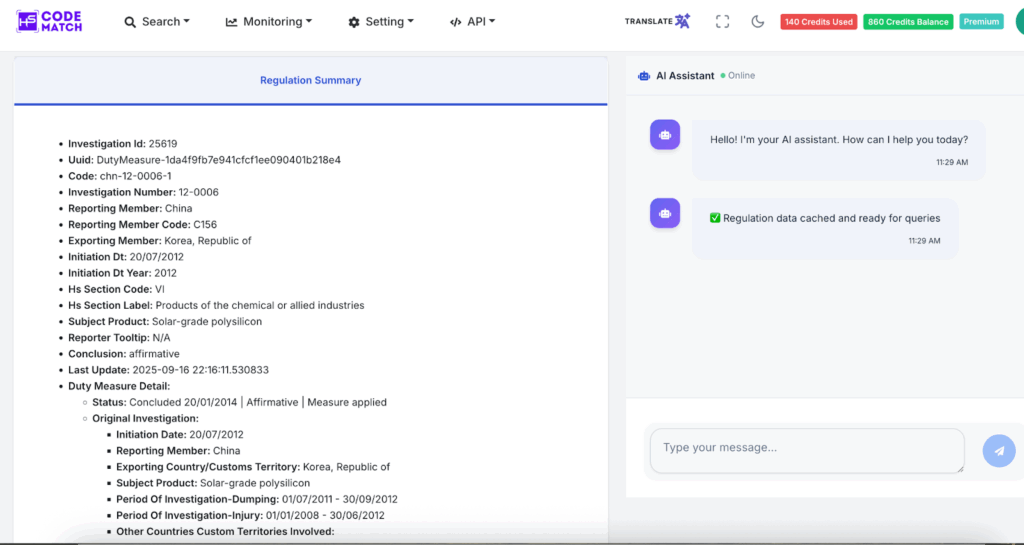
This is an example of antidumping measures that have been imposed by the Chinese government on the product of solar-grade polysilicon from South Korea. This summary includes the date the antidumping comes into effect and the last update related to this measure. Also, the measurement and the final determination of this product, as well as the most important things, are the duty rate.
Search FTA Rates and Rules of Origin Provisions
HS Code Match also provides the Search FTA Rates and Rules of Origin Provision. These features will help you to find the FTA rates based on the agreement between the origin country and the destination country. You can find this in the detailed information after you have looked for a specific country. This is an example of HS Code Match on tariff rates, the rule of origin, and the certificate provision in the United Kingdom based on the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPATTP) agreement.
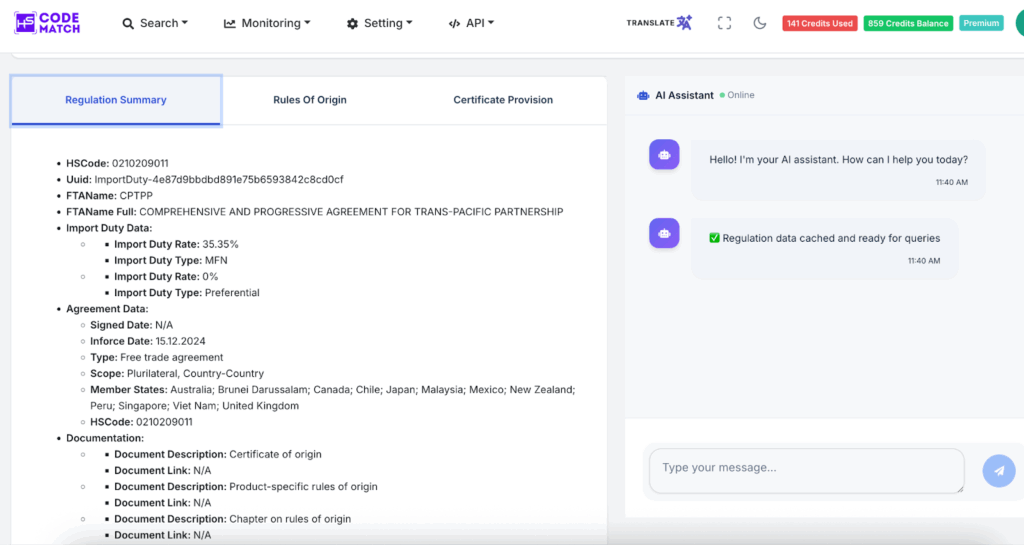
This detailed information shows a regulation summary, which shows that the import duty rate is 35,35 per cent, the HS code, and the member of the CPATTP, such as Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, Vietnam, and the UK. This summary also provides the lists of documentation for exporting the product and the HS description, which is an important part of the products that are subject to the latest FTA regulation.
In the rules of origin part, you can find the specific and full requirements for imported products from CPATTP in order to meet the criteria for entering the UK, including cumulation, de minimis, wholly obtained, etc. Then, the certificate provision, which contains the lists of requirements of a license from the agreement among the CPATTP member countries, you must obtain before exporting certain products to the UK.